1000 FAQs, 500 tutorials and explanatory videos. Here, there are only solutions!
Restore a snapshot on VPS Cloud
This guide explains how to restore a snapshot of VPS Cloud Infomaniak.
Warning: depending on the operating system installed, the system volume may be named /dev/sda, /dev/sda1 or /dev/vda; the same applies to the data volume /dev/sdb, /dev/sdb2 or /dev/vdb … It is therefore necessary to replace these indications with those corresponding to your situation.
Restore a snapshot
To do this:
- Click here to access the management of your product on the Infomaniak Manager (need help?).
- Click directly on the name assigned to the product concerned.
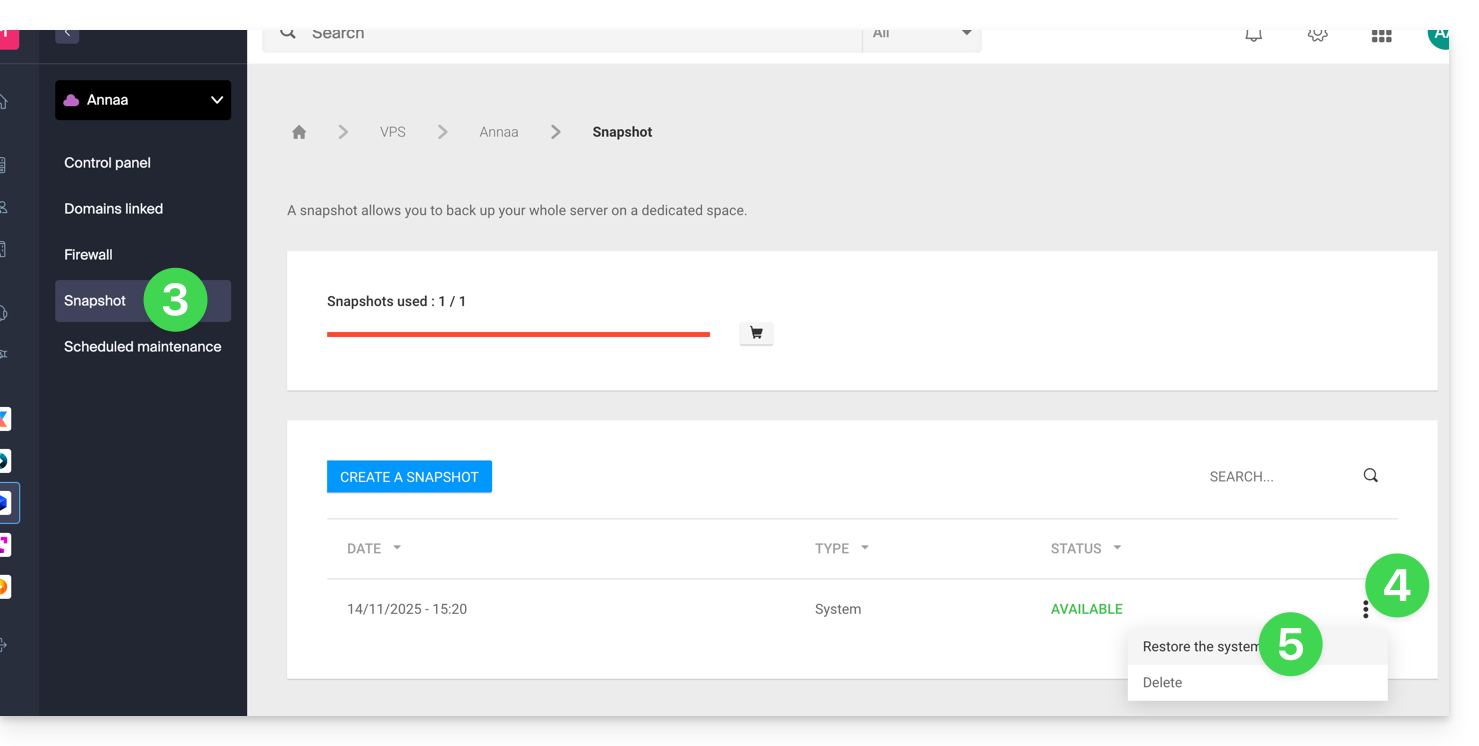
- Click on Snapshot in the left sidebar menu.
- Click on the action menu ⋮ to the right of the object concerned in the table that appears.
- Click on Restore:
- Click the blue button to start the snapshot restoration.
- An email is sent when the snapshot is restored.
Restore the operating system disk
Restoring the system volume as in the example above is an irreversible operation. The operating system disk will be replaced by the snapshot and the server will be in the exact state of the backup date.
The data stored on the data volume (vdb) is not affected by this operation.
Restore the data disk (vdb)
Two data restoration modes are possible:
1. “Read-only” mode
If the size of the snapshot differs from the size of the volume, only this read-only mode is available.
This option allows you to mount the snapshot data image, which allows read-only access to the backup data.
For information, here are useful commands to exploit your backup:
- To access the main data volume:
mount /dev/vdb /mnt/. - To mount the data volume in a specific folder "backup":
mount -o nouuid -o ro,norecovery /dev/vdc /backup.
To know which letter to use (/dev/vd?), use the command lsblk:
2. “Restore” mode
Restoring the data volume is an irreversible operation. The data disk (vdb) will be replaced by the snapshot. At the end of the restoration, it will be necessary to remount the data volume so that your operating system refreshes the content.
The following procedure and commands are provided for informational purposes only:
- Make sure your data volume is not mounted:
* umount /mnt(/mnt or the location you chose to access your data). - Remount the data volume:
* mount /dev/(vdb) /mnt
To know the name of the data volume attached to your server, use the command lsblk (see above).


