1000 FAQs, 500 tutorials and explanatory videos. Here, there are only solutions!
Manage the firewall for Web Hosting & Cloud Server
This guide explains how to allow certain incoming and/or outgoing ports in the firewall (firewall) of a Web hosting or a Cloud Server.
Preamble
- On a shared Web hosting, it is only possible to open outgoing ports.
- On a Cloud Server, it is possible to open incoming and outgoing ports.
- Opening ports allows certain applications to function properly but can reduce the security of your hosting.
Access the tool and add a rule
To manage port opening from the Manager:
- Click here to access the management of your hosting on the Infomaniak Manager (need help?).
- Click directly on the name assigned to the hosting concerned.
- Click on Security in the left sidebar.
- Click on Port Opening in the left sidebar.
- Click the Open a port button:
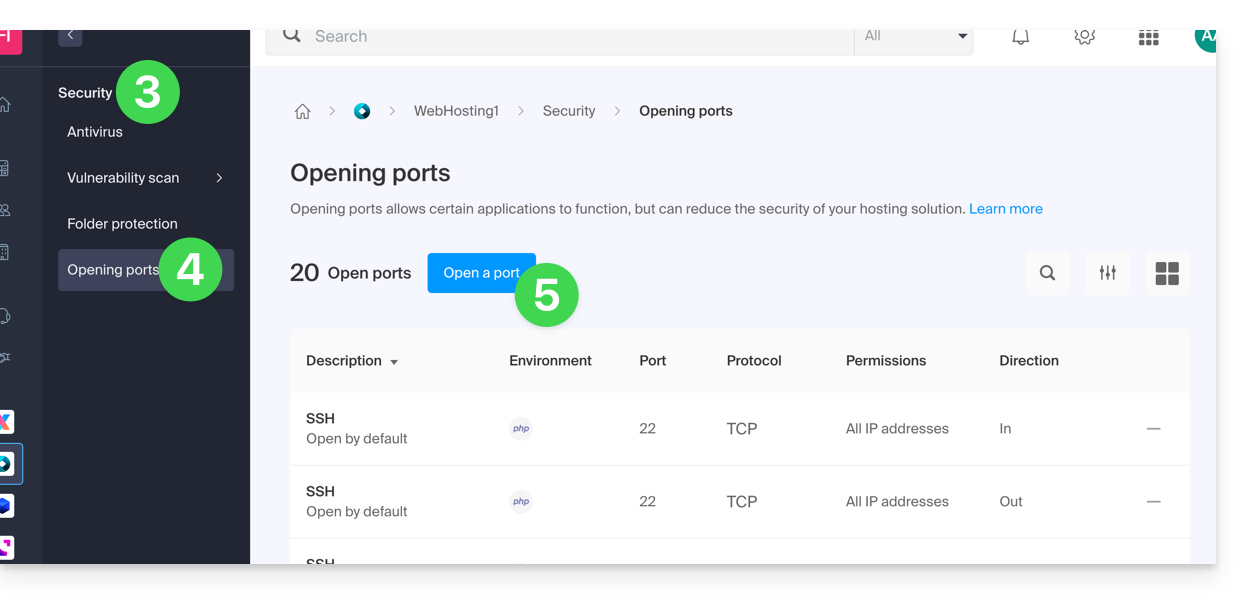
Open a port
It is only possible to set one port per rule, and only one IP / host per field: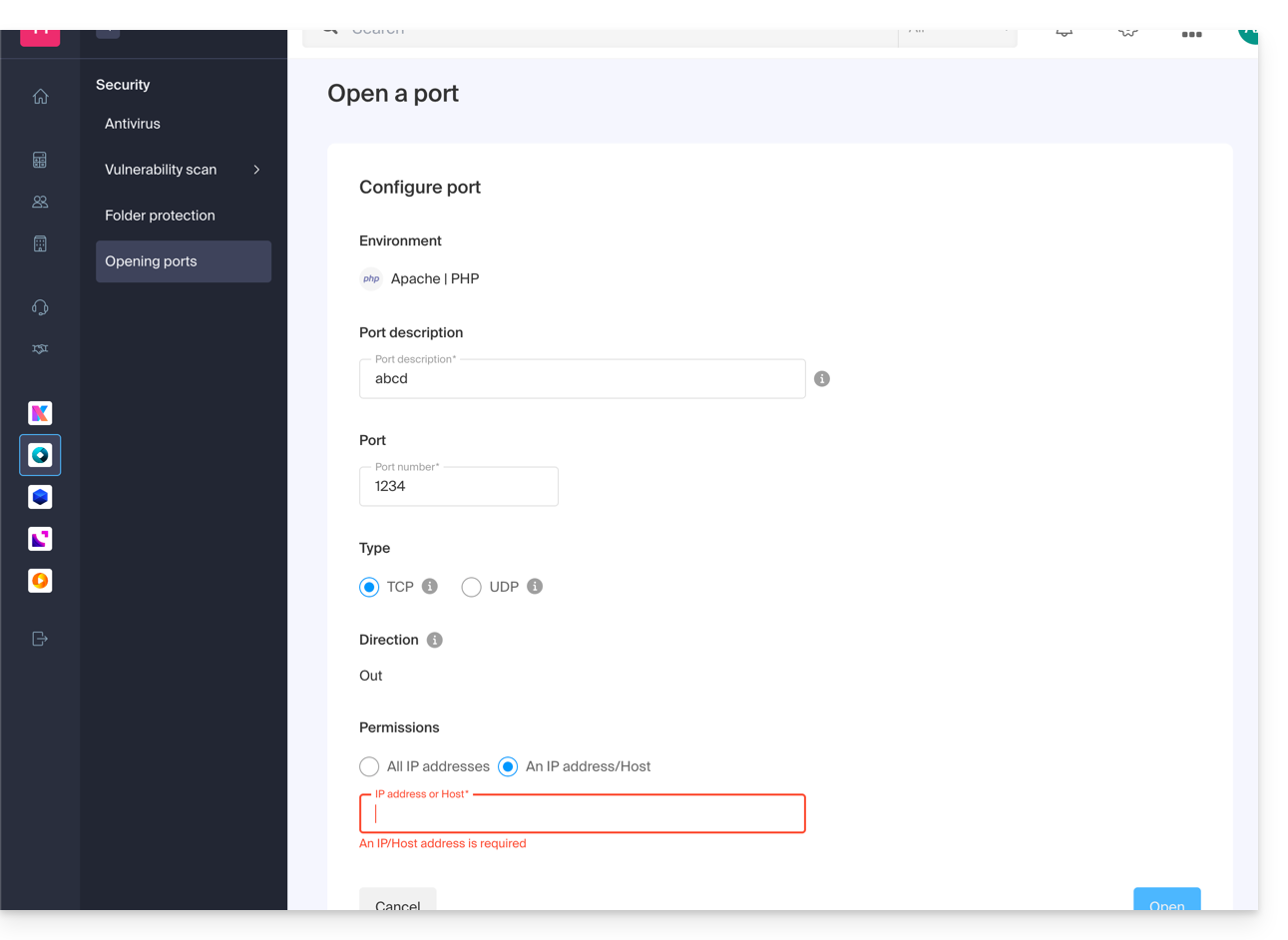
By specifying an IP or a host, the connection will only be allowed in these cases:
Incoming rule: if the connection comes from this IP or the specified hostOutgoing rule: if the connection is made to this IP or this host
Same for the "Type" of connection, if the protocol used for the connection is not the one specified in the rule, the connection is not allowed.
Open the outgoing port 25 globally
You can open the outgoing port 25 from the manager if a destination host is specified.
With a Cloud Server, to open this port to the world, contact Infomaniak support and justify your request.
Default open ports
Once you have accessed the port opening tool, you will find the list of default open ports on the page.
With a Cloud Server, to exceptionally close some of the listed ports, contact Infomaniak support and justify your request.
The display may sometimes be spread over several pages:
MySQL ports
Regarding database ports, refer to these guides:
Check the activity of a port (Cloud Server)
On Cloud Server, to check if an application is listening on a particular port (1234 in the example below) and to know the name of the application in question, run in SSH:
netstat -anpe | grep "1234" | grep "LISTEN"
